Input application for UGRAMM:
In a CGRA, the input application is usually represented as a Data Flow Graph (DFG), where vertices correspond to operations like ADD, SUB, and MUL, and the edges between these vertices indicate the dependencies among these operations. UGRAMM comes with various CGRA benchmarks designed for HPC applications, including Convolution, FFT, and Stencil, with both Balanced and Unbalanced versions. Additionally, each benchmark type supports different unrolling factors ranging from 1 to 10.
├── Kernels
├── Conv_nonBalance
├── Stencil_Balance
└── Stencil_nonBalance
├── Conv_nonBalance
│ ├── conv_nounroll_Any.dot
│ ├── conv_nounroll_nonBalance_Any.dot
│ ├── conv_nounroll_nonBalance_Specific.dot
│ ├── conv_nounroll_Specific.dot
│ ├── conv_unroll2_Any.dot
│ ├── conv_unroll2_nonBalance_Any.dot
│ ├── conv_unroll2_nonBalance_Specific.dot
│ ├── conv_unroll2_Specific.dot
│ ├── conv_unroll3_Any.dot
│ ├── conv_unroll3_nonBalance_Any.dot
│ ├── conv_unroll3_nonBalance_Specific.dot
│ └── conv_unroll3_Specific.dot
├── FFT-Radix-4
│ ├── fft_radix4_Any.dot
│ ├── fft_radix4_Specific.dot
│ ├── fft_radix4_unroll2_Any.dot
│ └── fft_radix4_unroll2_Specific.dot
├── FFT-Radix-5
│ ├── fft_radix5_Any.dot
│ └── fft_radix5_Specific.dot
- These benchmarks are defined in the Graphviz DOT format (ref).
//Node/Vertex definition:
FADD_19 [label="{FADD_19}", opcode=FADD, width=32];
FADD_18 [label="{FADD_18}", opcode=FADD, width=32];
//Edge definition:
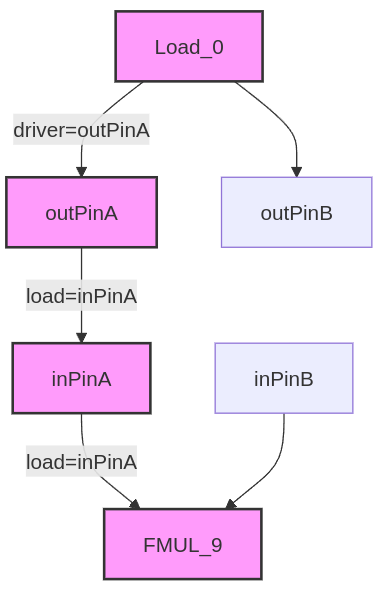
Load_0 -> FMUL_9 [driver=outPinA, load="inPinA"];
Load_1 -> FMUL_10 [driver=outPinA, load="inPinA"];
Required and optional attributes in application-dot file.
| Type | Required/Optional | Attribute | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Node | Required | label | Specifies the operation name in the application graph. | label="{Load_0}" |
| Node | Required | opcode | Specifies the operation’s opcode, indicating its functionality. | opcode="input" |
| Node | Optional | width | Specifies the width of the node for graphical representation. | width="5" |
| Edge | Required | driver | Specifies the driver pin to use for the edge connection. | driver="outPinA" |
| Edge | Required | load | Specifies the load pin to use for the edge connection. | load="inPinA" |
| Edge | Optional | latency | Specifies the latency requirement for the edge. | latency="2.0" |
Example Usage: Load_0 -> FMUL_9 [driver=outPinA, load=inPinA];
In this example, UGRAMM selects the outPinA of the device-model node where Load_0 is mapped and routes it to the inPinA of the device-model node where FMUL_9 is mapped. For UGRAMM to function as expected, the device model must have nodes with pins defined as outPinA, inPinA, B, etc.
The [Required] node and edge attributes must be clearly defined in the application.dot file (when used as an afile input) to ensure UGRAMM operates correctly.
Each CGRA-benchmark has two version in UGRAMM:
- Any: In this type,
loadPinsare not specified or constrained and default toAny2Pins. This serves as a useful comparison point with the classic GRAMM model. - Specific: This type includes benchmark where only a single
loadPinis specified.
Also, supported operations for both device-model and application-graph are defined as pragma which is defined within dot file itself which is covered here