Graph Vertex Generalization:
As outlined in the getting started guide, both the input application and hardware architecture are represented as graphs in UGRAMM. The vertex of the application graph (H) and device model graph (G) are designed to be versatile, making them applicable not only to CGRA applications but also adaptable to other use cases with minimal adjustments.
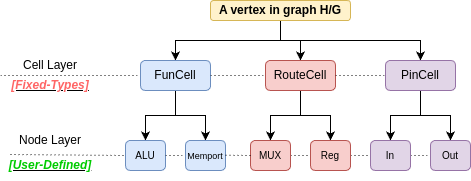
As shown in Fig.1, a vertex in graphs H or G can contain layered information describing its function:
- Cell Layer: Specifies if the vertex is used for routing or functional operations.
- Node Layer: Indicates the name/type of the node under the selected cell type.
- Supported Ops Layer: For functional cells (e.g.,
FuncCell), lists operations the cell supports.
CellType Categories
Each vertex must fall into one of these CellType categories:
- FuncCell: Represents a functional cell, typically performing operations such as arithmetic (e.g., ALU) or memory-related operations like load/store (e.g., IO/MemPort).
- RouteCell: Represents a routing cell, such as a multiplexer (MUX) or register, which is crucial for connecting two
FuncCells within the hardware. - PinCell: Represents a pin cell. Each functional cell must have defined input and output pins. For example, a 2-input ALU typically found in CGRA will have two input pins and one output pin in UGRAMM. UGRAMM utilizes these pins during the mapping process to manage properties such as commutativity when needed.
| Attribute | Description | Example Values |
|---|---|---|
| CellType [Fixed] | Defines the primary role of the vertex. | FuncCell, RouteCell, PinCell |
| NodeType [Generalized] | Defines the name/type of the vertex | ALU, MemPort, LUT, DSP |
| Supported Ops [Generalized] | Operations or opcodes that functional cells (FuncCell) can execute. | Add, Multiply, Store |
For a vertex, the CellType [Fixed] must be FuncCell, RouteCell, or PinCell, while the NodeType and SupportedOPs [Flexible] are user-defined (e.g., ALU, MemPort in CGRA or LUT, DSP in FPGA), these are parsed as attributes from input graphs in Graphviz DOT format.
Device-Model Vertex Examples:
The device model can incorporate all three CellType categories (FuncCell, RouteCell, PinCell) as shown below:
An ALU NodeType defined as a FuncCell is represented as follows:
50 [G_Name="pe.w32.c1.r0.alu", G_CellType=FuncCell, G_NodeType=ALU];
Similarly, other CellType and NodeType combinations are defined within the device model:
- A out (pin)
NodeTypedefined as aPinCellas follows:49 [G_Name="LS.w32.c7.r5.memport.outPinA", G_CellType=PinCell, G_NodeType=out];
- A MUX
NodeTypedefined as aRouteCellas follows:20 [G_Name="pe.w32.c1.r0.crossbar_mux_0", G_CellType=RouteCell, G_NodeType=Mux];
For additional details, refer to the device model file documentation.
Application-Graph Vertex Examples:
- As outlined in the application file input documentation, the application file defaults to having all vertices to be of
FuncCelltype. Other important attributes of this graph are also discussed there.
Also, supported operations for both device-model and application-graph are defined as pragma which is defined within dot file itself which is covered here